In this article we will connect a CCS811 gas sensor to a Linkit One and we will create an example using the Arduino IDE to display the values via web page and also a version which displays values on a web page
CCS811 is a low-power digital gas sensor solution, which integrates a gas sensor solution for detecting low levels of VOCs typically found indoors, with a microcontroller unit (MCU) and an Analog-to-Digital converter to monitor the local environment and provide an indication of the indoor air quality via an equivalent CO2 or TVOC output over a standard I2C digital interface.
Features
Integrated MCU
On-board processing
Standard digital interface
Optimised low power modes
IAQ threshold alarms
Programmable baseline
2.7mm x 4.0mm LGA package
Low component count
Proven technology platform
Specs
| Interface | I²C |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage [V] | 1.8 to 3.6 |
| Power Consumption [mW] | 1.2 to 46 |
| Dimension [mm] | 2.7 x 4.0 x 1.1 LGA |
| Ambient Temperature Range [°C] | -40 to 85 |
| Ambient Humidity Range [% r.h.] | 10 to 95 |
Parts List
| Amount | Part Type |
|---|---|
| 1 | CJMCU-811 CCS811 Air Quality Gas Sensor |
| 1 | LinkIt ONE MT2502A wireless 2503 development board |
Schematics/Layout
Remember and connect WAKE to gnd
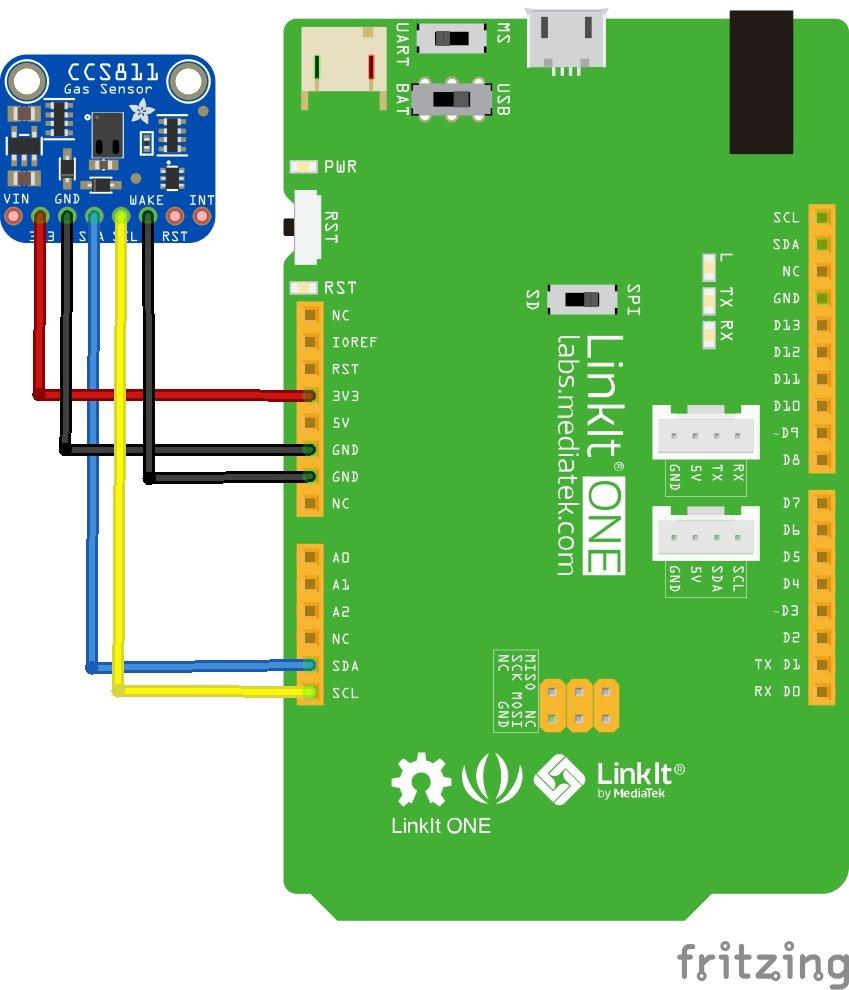
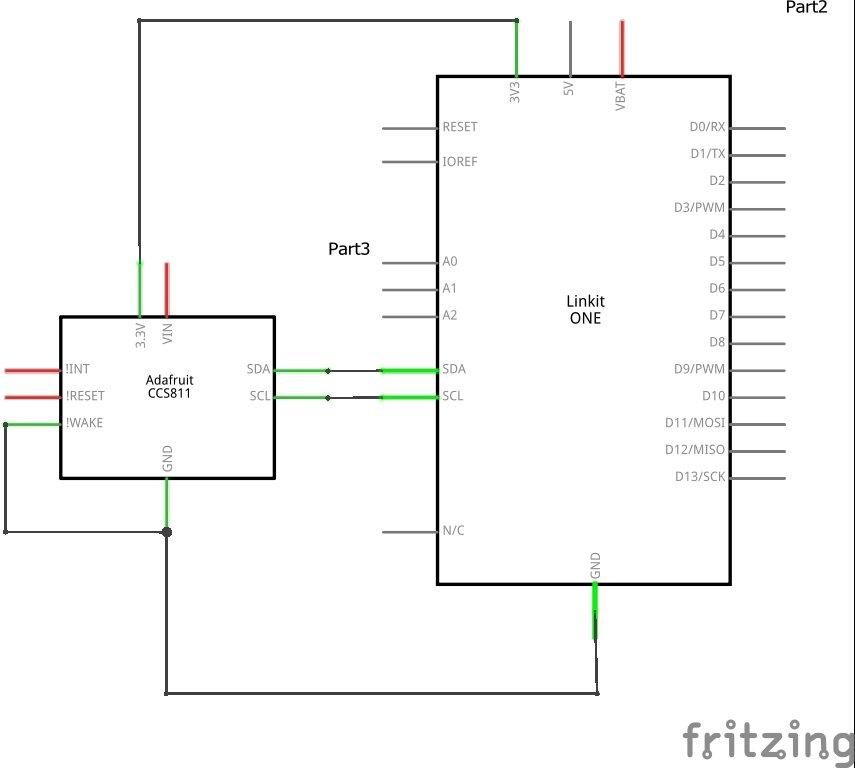
Code
Again we use a library – the adafruit CCS811 one, you can add this in the library manager
And this is the out of the box example
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include "Adafruit_CCS811.h"
Adafruit_CCS811 ccs;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("CCS811 test");
if(!ccs.begin())
{
Serial.println("Failed to start sensor! Please check your wiring.");
while(1);
}
//calibrate temperature sensor
while(!ccs.available());
float temp = ccs.calculateTemperature();
ccs.setTempOffset(temp - 25.0);
}
void loop()
{
if(ccs.available())
{
float temp = ccs.calculateTemperature();
if(!ccs.readData())
{
Serial.print("CO2: ");
Serial.print(ccs.geteCO2());
Serial.print("ppm, TVOC: ");
Serial.print(ccs.getTVOC());
Serial.print("ppb Temp:");
Serial.println(temp);
}
else
{
Serial.println("ERROR!");
while(1);
}
}
delay(500);
}
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open the serial monitor – this is what I saw. The higher CO2 level was when I breathed on the sensor
CO2: 400ppm, TVOC: 0ppb Temp:24.25
CO2: 400ppm, TVOC: 0ppb Temp:25.00
CO2: 400ppm, TVOC: 0ppb Temp:25.38
CO2: 1012ppm, TVOC: 93ppb Temp:25.38
CO2: 424ppm, TVOC: 3ppb Temp:25.00
CO2: 400ppm, TVOC: 0ppb Temp:25.38
CO2: 400ppm, TVOC: 0ppb Temp:24.25
CO2: 400ppm, TVOC: 0ppb Temp:13.68
WIFI Example
There are 3 lines that will/may need changed for your Wifi details
#define WIFI_AP "wifi ssid here" #define WIFI_PASSWORD "password here" #define WIFI_AUTH LWIFI_WPA The last one you can select from from LWIFI_OPEN, LWIFI_WPA, or LWIFI_WEP according to your WiFi AP configuration
[codesyntax lang=”cpp”]
#include <LTask.h>
#include <LWiFi.h>
#include <LWiFiServer.h>
#include <LWiFiClient.h>
#include "Adafruit_CCS811.h"
#define WIFI_AP "wifi ssid here"
#define WIFI_PASSWORD "password here"
#define WIFI_AUTH LWIFI_WPA
Adafruit_CCS811 ccs;
LWiFiServer server(80);
void setup()
{
LTask.begin();
LWiFi.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
if(!ccs.begin())
{
Serial.println("Failed to start sensor! Please check your wiring.");
//calibrate temperature sensor
while(!ccs.available());
float temp = ccs.calculateTemperature();
ccs.setTempOffset(temp - 25.0);
}
// keep retrying until connected to AP
Serial.println("Connecting to AP");
while (0 == LWiFi.connect(WIFI_AP, LWiFiLoginInfo(WIFI_AUTH, WIFI_PASSWORD)))
{
delay(1000);
}
printWifiStatus();
Serial.println("Start Server");
server.begin();
Serial.println("Server Started");
}
int loopCount = 0;
void loop()
{
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
delay(500);
loopCount++;
LWiFiClient client = server.available();
if (client)
{
Serial.println("new client");
// an http request ends with a blank line
boolean currentLineIsBlank = true;
unsigned long timer_out = millis();
while (client.connected())
{
if(millis()-timer_out > 5000)break;
if (client.available())
{
// we basically ignores client request, but wait for HTTP request end
int c = client.read();
Serial.print((char)c);
if (c == '\n' && currentLineIsBlank)
{
Serial.println("send response");
// send a standard http response header
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println("Connection: close"); // the connection will be closed after completion of the response
client.println("Refresh: 5"); // refresh the page automatically every 5 sec
client.println();
client.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML>");
client.println("<html>");
// output the value of each analog input pin
if(ccs.available())
{
float temp = ccs.calculateTemperature();
if(!ccs.readData())
{
client.print("CO2: ");
client.print(ccs.geteCO2());
client.print("ppm, TVOC: ");
client.print(ccs.getTVOC());
client.print("ppb Temp:");
client.println(temp);
}
else
{
client.println("ERROR!");
while(1);
}
}
break;
}
if (c == '\n')
{
// you're starting a new line
currentLineIsBlank = true;
}
else if (c != '\r')
{
// you've gotten a character on the current line
currentLineIsBlank = false;
}
}
}
// give the web browser time to receive the data
delay(500);
// close the connection:
Serial.println("close connection");
client.stop();
Serial.println("client disconnected");
}
}
void printWifiStatus()
{
// print the SSID of the network you're attached to:
Serial.print("SSID: ");
Serial.println(LWiFi.SSID());
// print your WiFi shield's IP address:
IPAddress ip = LWiFi.localIP();
Serial.println("Please open your browser, and input the following address:");
Serial.println(ip);
Serial.print("\r\nsubnet mask: ");
Serial.println(LWiFi.subnetMask());
Serial.print("gateway IP: ");
Serial.println(LWiFi.gatewayIP());
// print the received signal strength:
long rssi = LWiFi.RSSI();
Serial.print("signal strength (RSSI):");
Serial.print(rssi);
Serial.println(" dBm");
}
[/codesyntax]
This example has test code to help you out – the printWifiStatus function, open up the USB Modem Port – not the programming port. You should see a message like this
Connecting to AP
SSID: your ssid here
Please open your browser, and input the following address:
192.168.1.15
Now open the IP address above using your favourite web browser and you should see something like this
CO2: 564ppm, TVOC: 24ppb Temp:91.23
Links
CJMCU-811 CCS811 Air Quality Gas Sensor

