The ADXL345 is well suited for mobile device applications. It measures the static acceleration of gravity in tilt-sensing applications, as well as dynamic acceleration resulting from motion or shock. Its high resolution (4 mg/LSB) enables measurement of inclination changes less than 1.0°.
Several special sensing functions are provided. Activity and inactivity sensing detect the presence or lack of motion and if the acceleration on any axis exceeds a user-set level. Tap sensing detects single and double taps. Free-fall sensing detects if the device is falling.
These functions can be mapped to one of two interrupt output pins. An integrated, patent pending 32-level first in, first out (FIFO) buffer can be used to store data to minimize host processor intervention.
Features
- Ultralow power: as low as 23 μA in measurement mode and 0.1 μA in standby mode at VS = 2.5 V (typical)
- Power consumption scales automatically with bandwidth
- User-selectable resolution
- Fixed 10-bit resolution
- Full resolution, where resolution increases with g range, up to 13-bit resolution at ±16 g (maintaining 4 mg/LSB scale factor in all g ranges)
Parts List
Connection
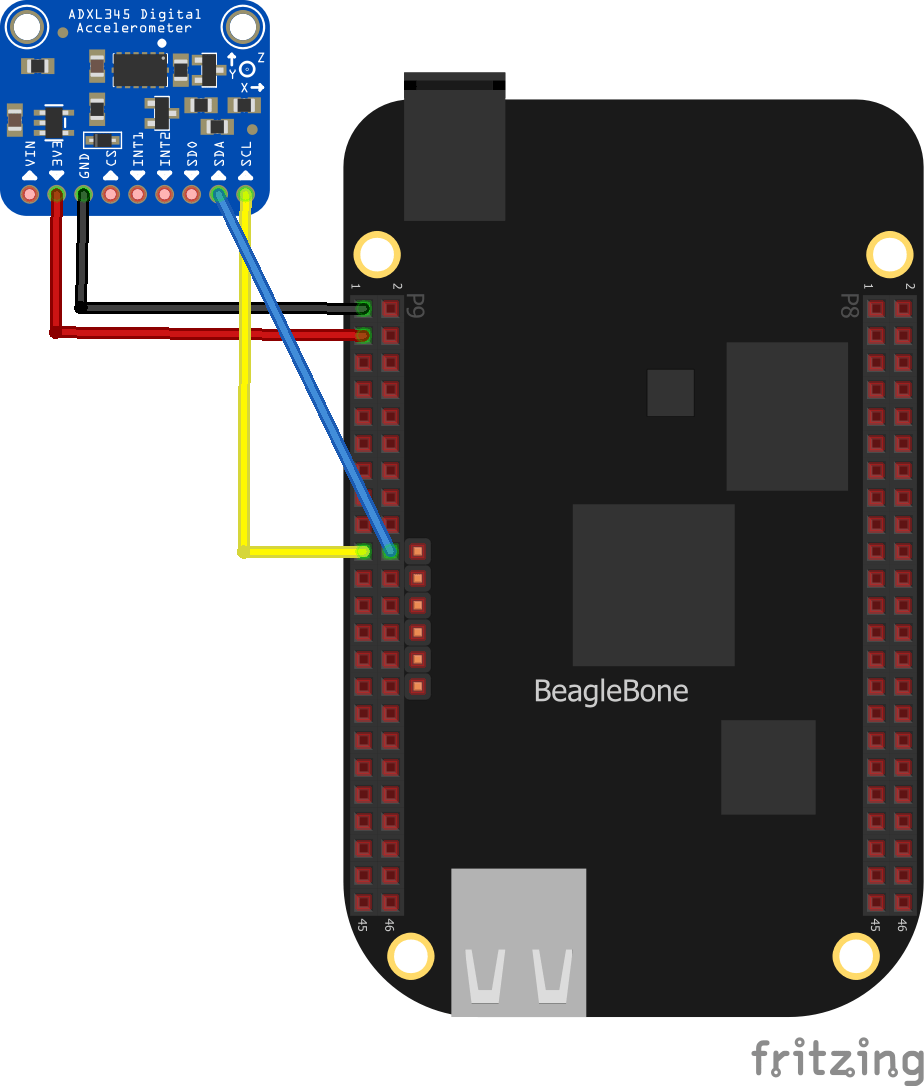
I used the following connection from the module above to my Beaglebone
| PI Connection | Module Connection |
| 3v3 | P9.3 |
| Gnd | P9.1 |
| SDA | P9.20 |
| SCL | P9.19 |
This is a layout showing the connection
Code
You need to save this as adxl345.py, I used the cloud9 IDE
[codesyntax lang=”python”]
import smbus
from time import sleep
bus = smbus.SMBus(2)
# ADXL345 constants
EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2 = 9.80665
SCALE_MULTIPLIER = 0.004
DATA_FORMAT = 0x31
BW_RATE = 0x2C
POWER_CTL = 0x2D
BW_RATE_1600HZ = 0x0F
BW_RATE_800HZ = 0x0E
BW_RATE_400HZ = 0x0D
BW_RATE_200HZ = 0x0C
BW_RATE_100HZ = 0x0B
BW_RATE_50HZ = 0x0A
BW_RATE_25HZ = 0x09
RANGE_2G = 0x00
RANGE_4G = 0x01
RANGE_8G = 0x02
RANGE_16G = 0x03
MEASURE = 0x08
AXES_DATA = 0x32
class ADXL345:
address = None
def __init__(self, address = 0x53):
self.address = address
self.setBandwidthRate(BW_RATE_100HZ)
self.setRange(RANGE_2G)
self.enableMeasurement()
def enableMeasurement(self):
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, POWER_CTL, MEASURE)
def setBandwidthRate(self, rate_flag):
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, BW_RATE, rate_flag)
# set the measurement range for 10-bit readings
def setRange(self, range_flag):
value = bus.read_byte_data(self.address, DATA_FORMAT)
value &= ~0x0F;
value |= range_flag;
value |= 0x08;
bus.write_byte_data(self.address, DATA_FORMAT, value)
# returns the current reading from the sensor for each axis
#
# parameter gforce:
# False (default): result is returned in m/s^2
# True : result is returned in gs
def getAxes(self, gforce = False):
bytes = bus.read_i2c_block_data(self.address, AXES_DATA, 6)
x = bytes[0] | (bytes[1] << 8)
if(x & (1 << 16 - 1)):
x = x - (1<<16)
y = bytes[2] | (bytes[3] << 8)
if(y & (1 << 16 - 1)):
y = y - (1<<16)
z = bytes[4] | (bytes[5] << 8)
if(z & (1 << 16 - 1)):
z = z - (1<<16)
x = x * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
y = y * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
z = z * SCALE_MULTIPLIER
if gforce == False:
x = x * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
y = y * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
z = z * EARTH_GRAVITY_MS2
x = round(x, 4)
y = round(y, 4)
z = round(z, 4)
return {"x": x, "y": y, "z": z}
if __name__ == "__main__":
# if run directly we'll just create an instance of the class and output
# the current readings
adxl345 = ADXL345()
axes = adxl345.getAxes(True)
print "ADXL345 on address 0x%x:" % (adxl345.address)
print " x = %.3fG" % ( axes['x'] )
print " y = %.3fG" % ( axes['y'] )
print " z = %.3fG" % ( axes['z'] )
[/codesyntax]
Now create another file called test_adxl345.py and entering the following
[codesyntax lang=”python”]
from adxl345 import ADXL345
adxl345 = ADXL345()
axes = adxl345.getAxes(True)
print "ADXL345 on address 0x%x:" % (adxl345.address)
print " x = %.3fG" % ( axes['x'] )
print " y = %.3fG" % ( axes['y'] )
print " z = %.3fG" % ( axes['z'] )
[/codesyntax]
Output
Open a terminal in the Cloud9 IDE and enter python test_adxl345.py
debian@beaglebone:/var/lib/cloud9/iain$ python test_adxl345.py ADXL345 on address 0x53: x = -0.216G y = -0.388G z = 0.300G

